The phpMyAdmin is written on PHP. The current phpMyAdmin version is compatible with PHP 7.1 and newer and MySQL 5.5 or MariaDB 5.5 or newer. This tutorial will help you to install and configure phpMyAdmin on Ubuntu 20.04 Linux system.
Step 1 – Install Apache and PHP
We are assuming you already have installed the MySQL server on Ubuntu system. So just install the other required packages to run and access phpMyAdmin. Once the installation finished, enable and start Apache web server.
Step 2 – Install phpMyAdmin on Ubuntu 20.04
phpMyAdmin is also available under the default packages repository but mostly they have older version. In this tutorial, we will download latest phpMyAdmin and configure on our system. Your system is ready for the phpMyAdmin installation. Download the latest phpMyAdmin archive from the official download page, or use the below commands to download phpMyAdmin 5.1.1 on your system. After downloading extract archive and move to the proper location. Next, create tmp directory and set the proper permissions.
Step 3 – Configure phpMyAdmin
Now, you need to configure web server to serve phpMyAdmin on network. Create Apache configuration file for phpMyAdmin and edit in text editor: add the below content to file.
Save your file. Press ESC key to switch to command more. Then type : (colon) and type w after the colon and hit Enter. After making all the changes, make sure to start the Apache service to reload all settings.
Step 4 – Adjusting FirewallD
The systems with enabled firewalls need to allow HTTP service from the firewall. Run the below commands to open a port for the webserver in the firewall.
Step 5 – Access phpMyAdmin
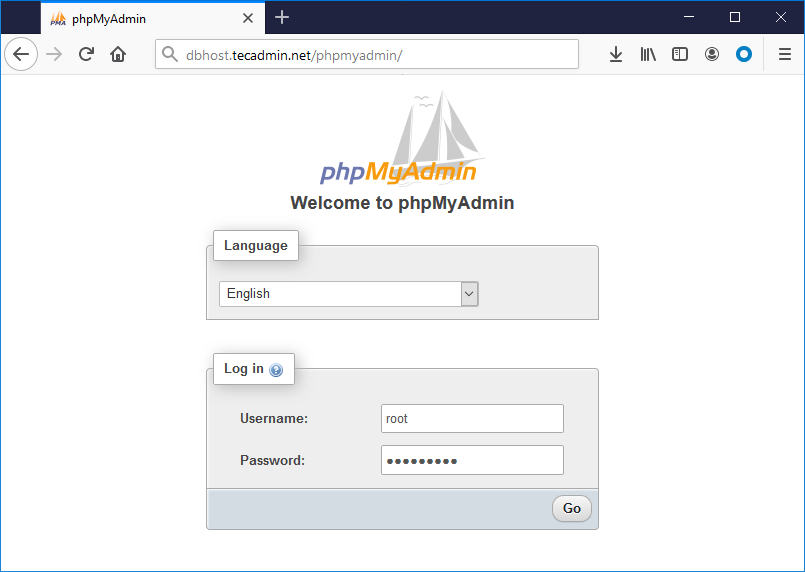
All done. You have finished the setup with the phpMyAdmin on Ubuntu Linux system. Now access phpMyAdmin with the server IP address or domain name. Replace your-server-ip-domain with the localhost (for the local machines), or system IP address for remote machines. I have updated our DNS and pointed dbhost.tecadmin.net to the server’s IP address.
Log in with the username and password used to access MySQL on the command line.
Conclusion
You have successfully configured phpMyAdmin on Ubuntu system. Let’s disable root user login for the phpMyAdmin for security purposes.